Scorecards (Performance Cards), one of the building blocks of data-driven organizations, cab be used to track the progress of a whole organization as well as its parts. Leaders can identify potential problems and make timely amendments before they become destructive.
What is a scorecard?
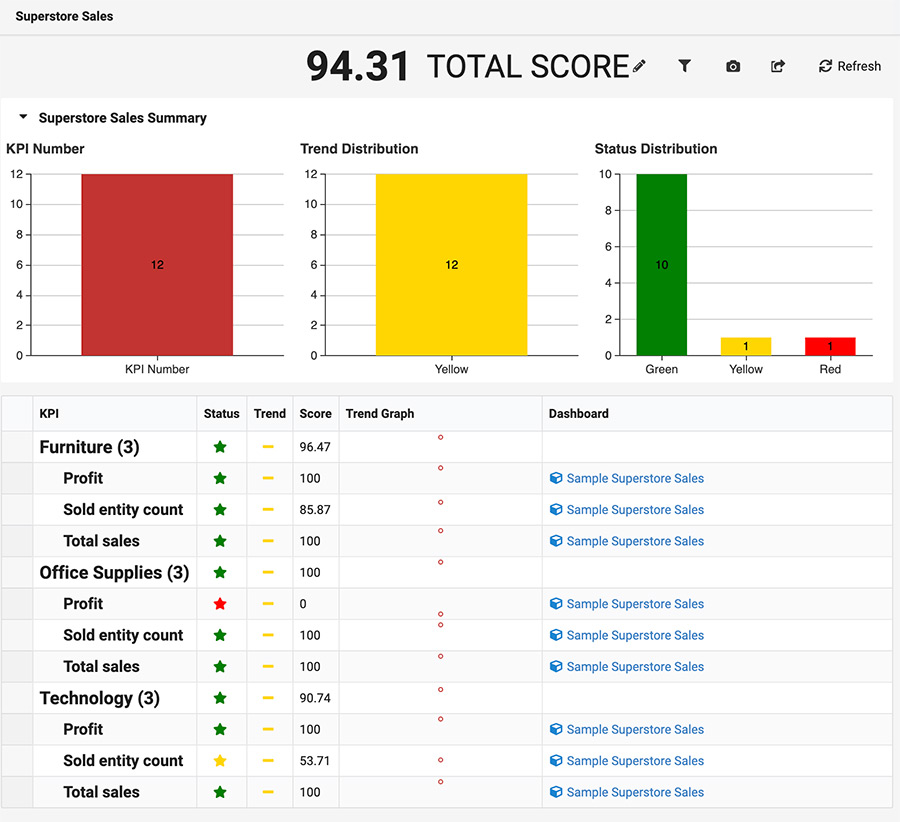
Above all, the scorecard is a management approach. Strategies are distilled into goals and goals into KPIs. KPIs are used to build TURBOARD scorecards (like dashlets are used to build dashboards). They can be linked to real-time data (utilized by the TURBOARD data model) or kept static for managers to fill periodically. See the sample scorecards at the bottom of the page.
Why are scorecards a valuable extension of classical dashboards?
| Dashboard | Scorecard | |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose of Usage |
|
|
| Measuring Method |
|
|
| Target Group |
|
|
| Data Update Period |
|
|
| Depth |
|
|
| Focus |
|
|
| Output |
|
|
What are the Main Components of a Scorecard?
Status Column
Presents a normalized score with its success rate, using colors or icons (that can be changed in configuration).
Trend Column
Presents the latest change in score of a given KPI.
Score Column
The score is calculated with the value of KPIs in that group (or normalized/atomic value if it's leaf node).
Calculation
- Min-Max range.
- Weight: some KPIs are more important than others. You can adjust their relative importance by adjusting their weight.
- Aim direction: as an example, a lower smoking rate is better for health but a higher smoking rate is better for the profit of a tobacco company.
To reveal striking insights hidden in your own data, discover